NNI review article from Zhihu:
The article is by a NNI user on Zhihu forum. In the article, Garvin had shared his experience on using NNI for Automatic Feature Engineering. We think this article is very useful for users who are interested in using NNI for feature engineering. With author’s permission, we translated the original article into English.
source: 如何看待微软最新发布的AutoML平台NNI?By Garvin Li
01 Overview of AutoML¶
In author’s opinion, AutoML is not only about hyperparameter optimization, but also a process that can target various stages of the machine learning process, including feature engineering, NAS, HPO, etc.
02 Overview of NNI¶
NNI (Neural Network Intelligence) is an open source AutoML toolkit from Microsoft, to help users design and tune machine learning models, neural network architectures, or a complex system’s parameters in an efficient and automatic way.
Link: https://github.com/Microsoft/nni
In general, most of Microsoft tools have one prominent characteristic: the design is highly reasonable (regardless of the technology innovation degree). NNI’s AutoFeatureENG basically meets all user requirements of AutoFeatureENG with a very reasonable underlying framework design.
03 Details of NNI-AutoFeatureENG¶
The article is following the github project: https://github.com/SpongebBob/tabular_automl_NNI.
Each new user could do AutoFeatureENG with NNI easily and efficiently. To exploring the AutoFeatureENG capability, downloads following required files, and then run NNI install through pip.

NNI treats AutoFeatureENG as a two-steps-task, feature generation exploration and feature selection. Feature generation exploration is mainly about feature derivation and high-order feature combination.
04 Feature Exploration¶
For feature derivation, NNI offers many operations which could automatically generate new features, which list as following :
count: Count encoding is based on replacing categories with their counts computed on the train set, also named frequency encoding.
target: Target encoding is based on encoding categorical variable values with the mean of target variable per value.
embedding: Regard features as sentences, generate vectors using Word2Vec.
crosscout: Count encoding on more than one-dimension, alike CTR (Click Through Rate).
aggregete: Decide the aggregation functions of the features, including min/max/mean/var.
nunique: Statistics of the number of unique features.
histsta: Statistics of feature buckets, like histogram statistics.
Search space could be defined in a JSON file: to define how specific features intersect, which two columns intersect and how features generate from corresponding columns.
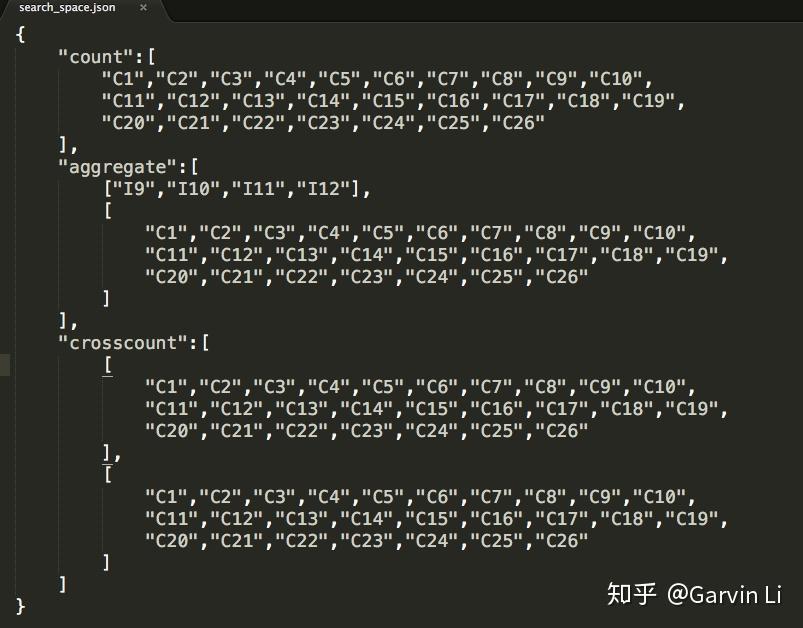
The picture shows us the procedure of defining search space. NNI provides count encoding for 1-order-op, as well as cross count encoding, aggerate statistics (min max var mean median nunique) for 2-order-op.
For example, we want to search the features which are a frequency encoding (valuecount) features on columns name {“C1”, …,” C26”}, in the following way:

we can define a cross frequency encoding (value count on cross dims) method on columns {“C1”,…,”C26”} x {“C1”,…,”C26”} in the following way:

The purpose of Exploration is to generate new features. You can use get_next_parameter function to get received feature candidates of one trial.
RECEIVED_PARAMS = nni.get_next_parameter()
05 Feature selection¶
To avoid feature explosion and overfitting, feature selection is necessary. In the feature selection of NNI-AutoFeatureENG, LightGBM (Light Gradient Boosting Machine), a gradient boosting framework developed by Microsoft, is mainly promoted.
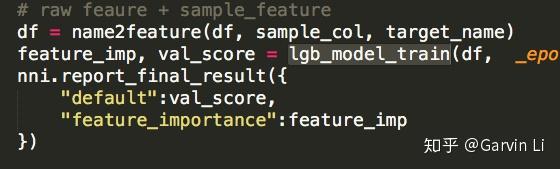
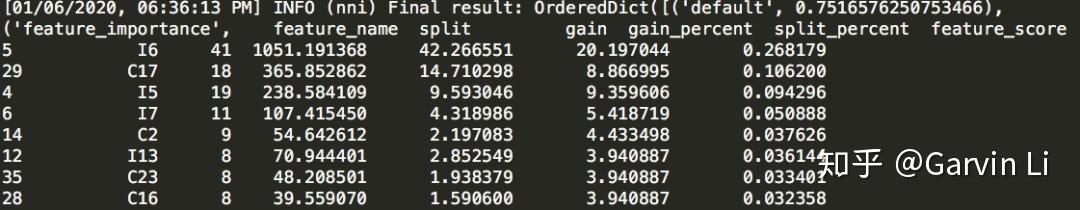
If you have used XGBoost or GBDT, you would know the algorithm based on tree structure can easily calculate the importance of each feature on results. LightGBM is able to make feature selection naturally.
The issue is that selected features might be applicable to GBDT (Gradient Boosting Decision Tree), but not to the linear algorithm like LR (Logistic Regression).
06 Summary¶
NNI’s AutoFeatureEng sets a well-established standard, showing us the operation procedure, available modules, which is highly convenient to use. However, a simple model is probably not enough for good results.
Suggestions to NNI¶
About Exploration: If consider using DNN (like xDeepFM) to extract high-order feature would be better.
About Selection: There could be more intelligent options, such as automatic selection system based on downstream models.
Conclusion: NNI could offer users some inspirations of design and it is a good open source project. I suggest researchers leverage it to accelerate the AI research.
Tips: Because the scripts of open source projects are compiled based on gcc7, Mac system may encounter problems of gcc (GNU Compiler Collection). The solution is as follows:
brew install libomp